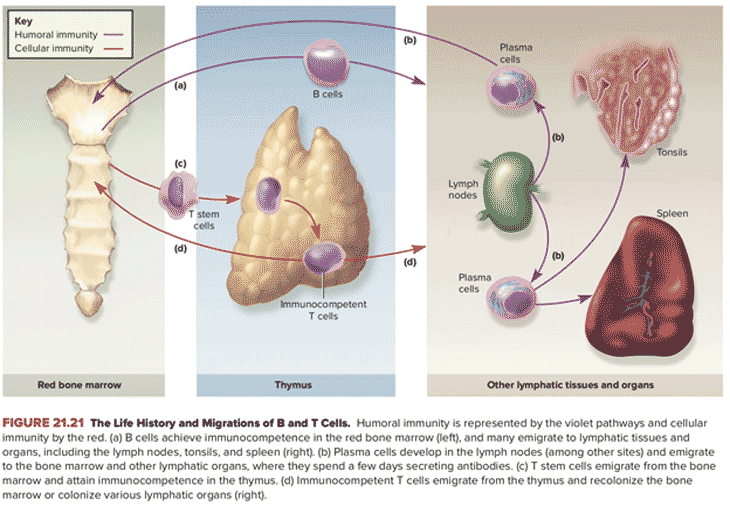
- Is the bilobate encapsulated organ located behind sternum.
- Is the main organ for T cell maturation and
- It stays extremely active within fetal stage (max) and continuously atrophies at puberty.
- It is made up of cortical, medullary epithelial cells, stromal cells, interdigitating cells and macrophages.
- All cells are important in the differentiation of migrated T cell precursors and their screening before their movement to secondary lymphoid tissues.
The function of the thymus:
- Several hormones produced by the thymus stimulate the
- maturation of the T cells in the bloodstream where they identify and destroy pathogens,
- activate B cells to produce antibodies, and
- store the memory of past infections.